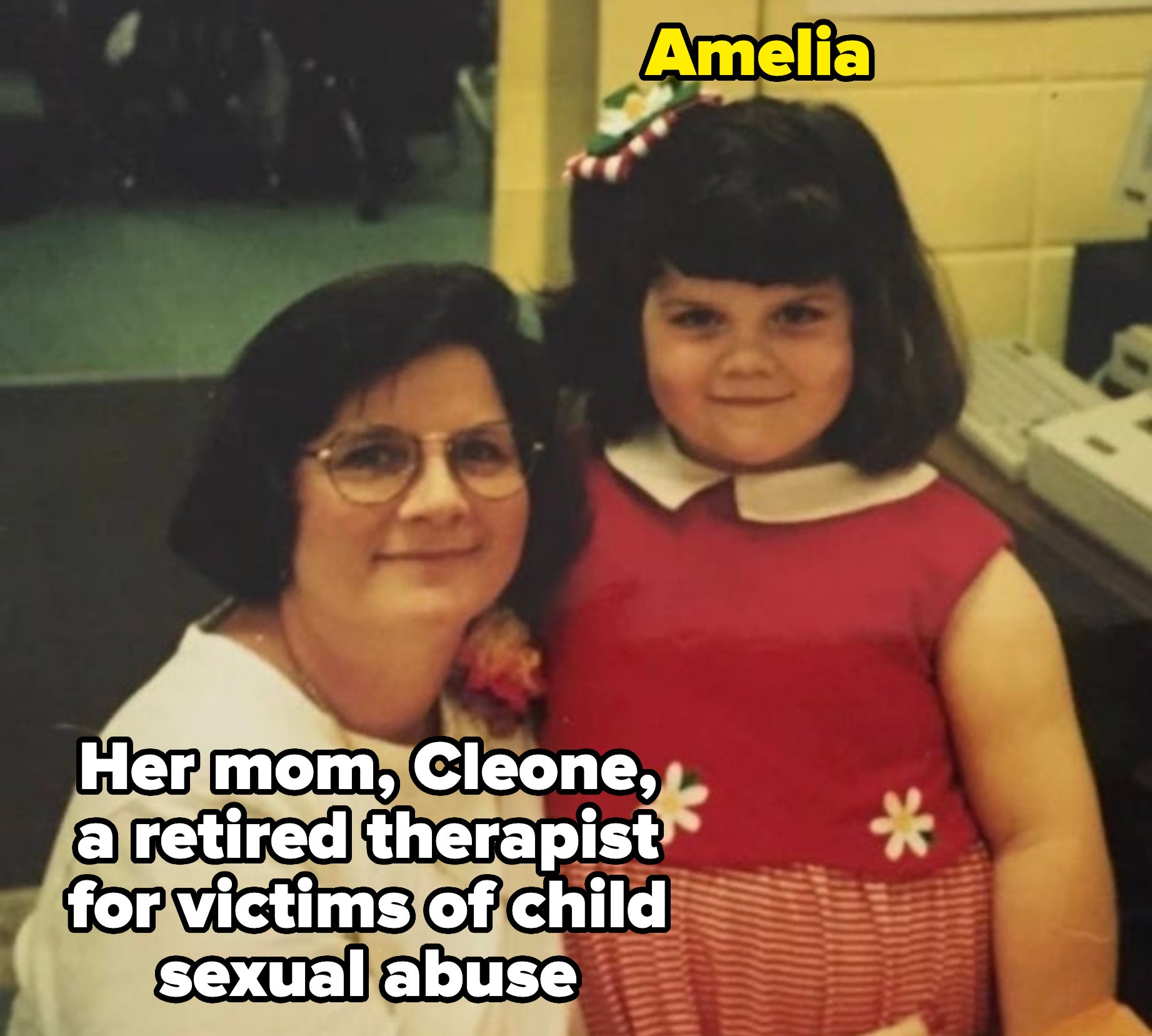" I wanted to talk about this because of the Nickelodeon docudrama that just came out , which I ’m so beaming people are paying attention to . "
monition : discussion of child sexual maltreatment .
It’s been a few weeks sinceQuiet on Set: The Dark Side of Kids TVexposedthe allegedly exploitative, toxic, and sexually abusive culture Nickelodeon’s early-aughts child stars faced.
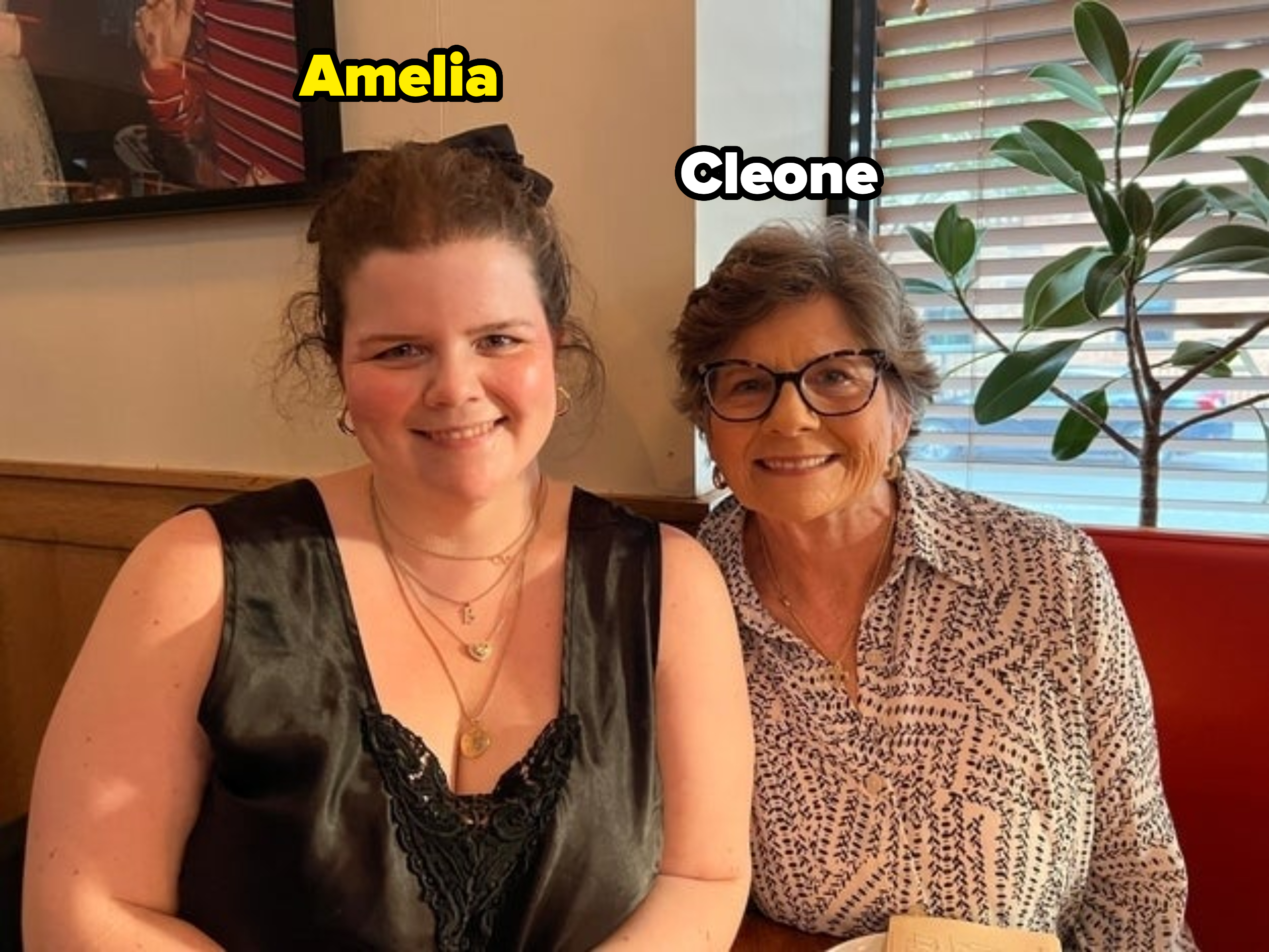
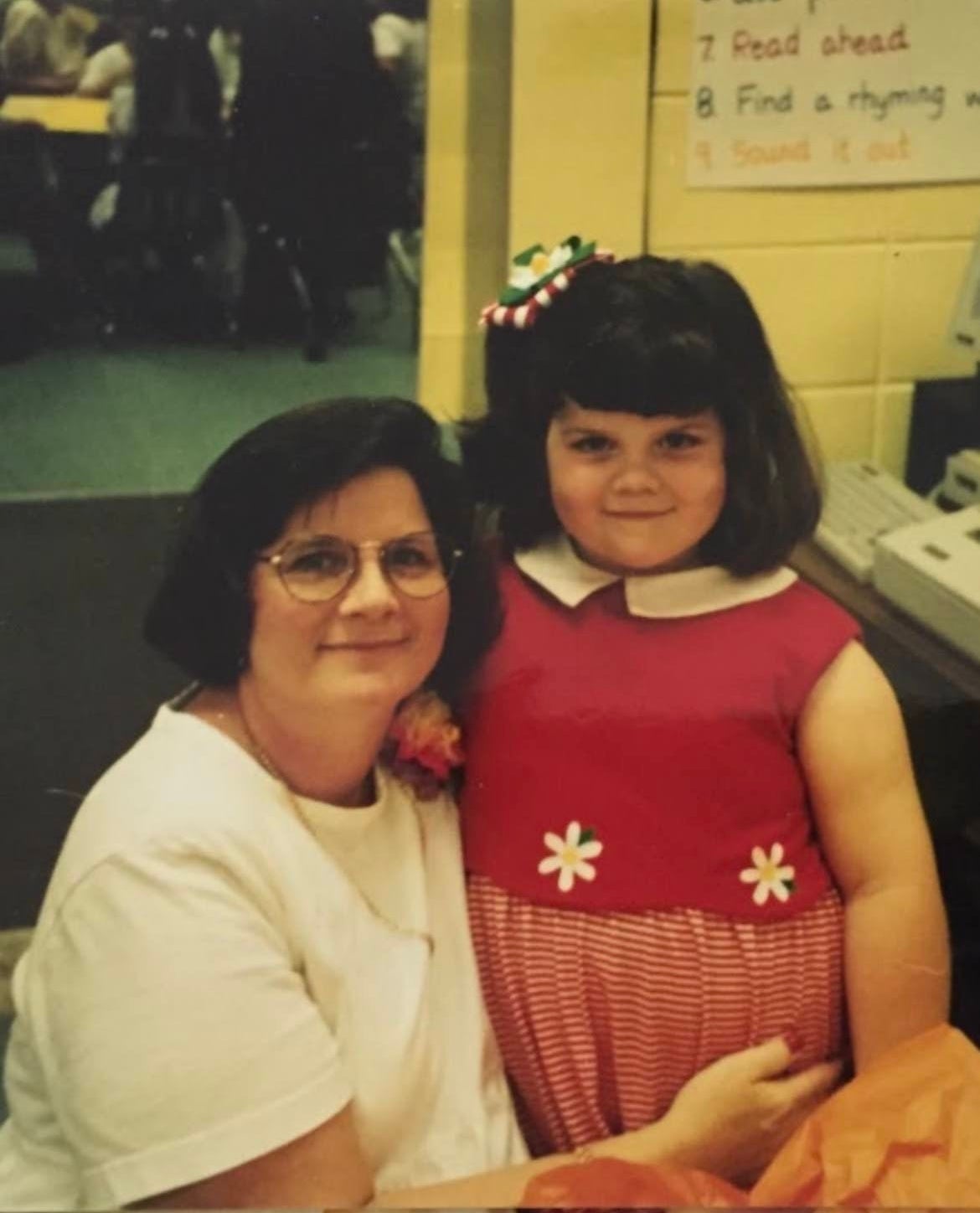
Amidst the conversation, Amelia Brock — a 33-year-old daughter of retired child sexual abuse therapist, Cleone Brock —shared on TikTokthe importance of educating children about sex and body safety.
Ameliabegan, “I am the daughter of a therapist for victims of child sexual abuse. And I want to tell you about all the things that my mom did when I was growing up to educate me and prevent me from being in a situation where I’d be sexually abused.”
So, let’s get into the five areas Amelia shared that we need to “tackle or disrupt” to be more effective in child sexual abuse prevention:
1. Access
Amelia said that thinking about when adults will have complete access to kids is essential, but she also admitted that this doesn’t mean parents must restrict sleepovers completely.
2. Knowledge gap
Amelia continued, “The way that my mom tackled this was from the time I was little, she had a picture book about sex that taught me about anatomy, about genitals, about what sex was. Obviously, it was age-appropriate; it was not graphic. And it was to teach me about what these things were.”
She continued, “But how is a child toknowthat? An adult is telling them to participate in this activity and forcing them to.”
" So kid need to hump what sex is , and that it ’s not appropriate for them to participate in it … that it ’s not appropriate for an grownup to touch their body in certain way , and it should never make them sense sorry or ashamed . And that if it does , then that ’s something that needs to be severalize to mom or dad . "
3. Disrupting silence
“It always shocks me how many parents in passing will be like, ‘Don’t ever let anybody touch you. Tell me, right?’ And it’s like, what’s the kid supposed to feel? You’re, like, halfway yelling at them, right? That’s not a conversation.”
Amelia admitted, “If you do not set up that space with your child, [and] something happens to them like sexual abuse, why would they tell you about it? You haven’t proven yourself to them as a trusted person in their life who’s taking care of their emotional well-being.”
" And until you turn out that , then it ’s very unlikely that your child is become to confide in you in that path . So that is something that need to be happening over and over again . And it needs to be testify through action , not just words . Not say you may secern me anything;prove itto them . "
4. Disrupting shame
She continued, “Part of that, too, in my conversations with my mom, was her taking me through exactly what would happen if I ever came to her and said, ‘This has happened to me,’ or, ‘This adult made me feel uncomfortable,’ or, ‘This adult tried to touch me.'”
Amelia said, “I knew that, you know, I knew in my core if something like that were to happen to me, my mom would respond to me with love and care because she had proven it.”
5. Compliance
She said, “This is not putting the onus on the child to get out of a situation in which an adult is trying to harm them, but it is letting them know thatthey have inside feelingsthat can give their brain information about when they might be in a situation that is not good for them, or where harm may occur.”
Amelia clarified, “Obviously, you know, have that conversation the way that’s most appropriate with your child. But so much of what we tell kids is, ‘Sit your ass in your seat and be good in school and pay attention to the adults and do everything they say.’ That is a very, very harmful construct, unless you give nuance with your child.”
“So, [it’s about] disrupting that [compliance] framework and letting a child know that they have agency, and especially that they have the agency to listen to what their body and their feelings are telling them, and to listen to this information that their parents have been telling them, and to leave situations that they don’t feel comfortable with. To say, ‘I want my mom.’ To call mom. To bring a parent into it. That is all really, really important.”
As for why she started sharing this in the first place, Amelia saidQuiet on Setwas a huge catalyst, but she wanted to hear more conversations about prevention, which she had direct experience with. Amelia told BuzzFeed, “On TikTok, I’ve seen so many brave personal accounts about enduring child sexual abuse. But I haven’t seen many videos about how to educate your child and have preventative conversations.”
And that it did — since sharing her video, Amelia has received an outpour of support, with many commenters thankful to see someone speaking about this.
And if you’re coming across this information for the first time, you might be wondering how even to begin these conversations with your kids. So, we spoke with Amelia and her mom, Cleone, to better understand how to broach these conversations.
Cleone began, “The first step really depends on your child’s age. Ask questions to see what they already know. You don’t have to start with a full anatomy lesson or explaining sex. Ask your child if they know what areas are private on a person’s body. Ask if anyone has ever tried to touch their private areas, talked to them about those areas, asked to take photos, or has even made them feel uncomfortable on these topics.”
Cleone continued, “Teach your child about healthy secrets vs. unhealthy secrets — a surprise birthday party is a healthy secret that doesn’t hurt anyone, and we feel good inside when we keep that secret. A friend telling them that someone has touched them inappropriately is not a healthy secret, and keeping that secret makes us feel bad inside. Underscore that telling a trusted adult about unhealthy secrets is important because it’s the only way a bad situation can be stopped.”
“The key here is creating a space where you and your child can have open dialogue, and they don’t feel scared to talk to you, which is a common silencing tactic used by abusers. Ultimately, your child needs to know that you will always answer their questions truthfully, and they will never be in trouble for confiding in you,” Cleone said.
As for when to begin having these conversations with your children, Cleone said that around 3 or 4 years old, you can start teaching your child about body safety, but also take clues based on your child’s questions. She said, “Young children need to know what is private about their own bodies and other people’s bodies. This doesn’t have to be a conversation about genitalia, yet; you can use photos of people in bathing suits to identify private areas.”
Amelia reiterated to BuzzFeed that her mom normalized these conversations by making them recurring and an open space for questions, which, as Cleone mentioned, would often guide what they would talk about. Amelia said, “Kids are very curious… I don’t remember thinking it was weird or scary to have these conversations, because it was normal at our house.”
And while Amelia said these conversations didn’t necessarily become more normalized with her peers, she said they did help her understand “dangerous secrets,” and to always speak up if she ever heard of any sexual abuse.
Cleone added that while Amelia summed up a lot of their early conversations in just a few minutes, she wants to remind people that those conversations happened over many years.
She said , " Our discussions were often point by her questions , and I think the most of import thing was reply frankly and form sure she felt well-off talk about everything with me . "
If you’re looking for more resources on the topic, Cleone saidthe Child Advocacy Centeris a great place to start. She also said the organizationDarkness to Lighthas statistics about CSA that parents can learn from, like how often abuse happens, who’smost likely tobe an abuser, and when and where it’s most common.
She tally , " Also , it ’s always a good idea to ask your local bibliothec about current Book and resource . They ’ll recognize what ’s years and developmentally appropriate for your Kid . " finally , if you ’re concerned about a sexual maltreatment situation with a baby , Cleone said , " Call yourlocal Child Advocacy Center . They will help you assess and voyage the situation , include reporting and therapy . "
Amelia had just one last thing to add: “I’m so grateful to my mom — for having these conversations with me, for being a wonderful parent, for helping so many children and truly seeing them when other people would rather look away, and for testifying against so many abusers over the years.”
If you or someone you love has see sexual violation , you may call theNational Sexual Assault Hotlineat 1 - 800 - 656 - HOPE ( 4673 ) , which rootle the company to their nearest intimate assault service supplier . you could also search for your local centerhere . If you are concerned that a tike is experiencing or may be in danger of abuse , you could call or text theNational Child Abuse Hotlineat 1 - 800 - 422 - 4453 ( 4.A.CHILD ) ; service can be bring home the bacon in over 140 voice communication .
Per Cleone ’s advice : you could also find your local Child Advocacy Centerhere , who can help you report the situation and regain resources , let in therapy .